Understanding Density: A Comprehensive Guide
Key Takeaways
- Density is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, describing how much mass is contained in a given volume.
- It is crucial in various applications, from determining whether an object will float to understanding material properties.
- Density is calculated using the formula: Density = Mass/Volume.
- The concept of density extends beyond physical objects, applying to fields like population density in geography.
What is Density?
Density is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering that describes the amount of mass contained within a specific volume. This property is crucial for understanding how substances interact with each other and their environments. By definition, density is the ratio of mass to volume, typically expressed in units like kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
The Formula for Density
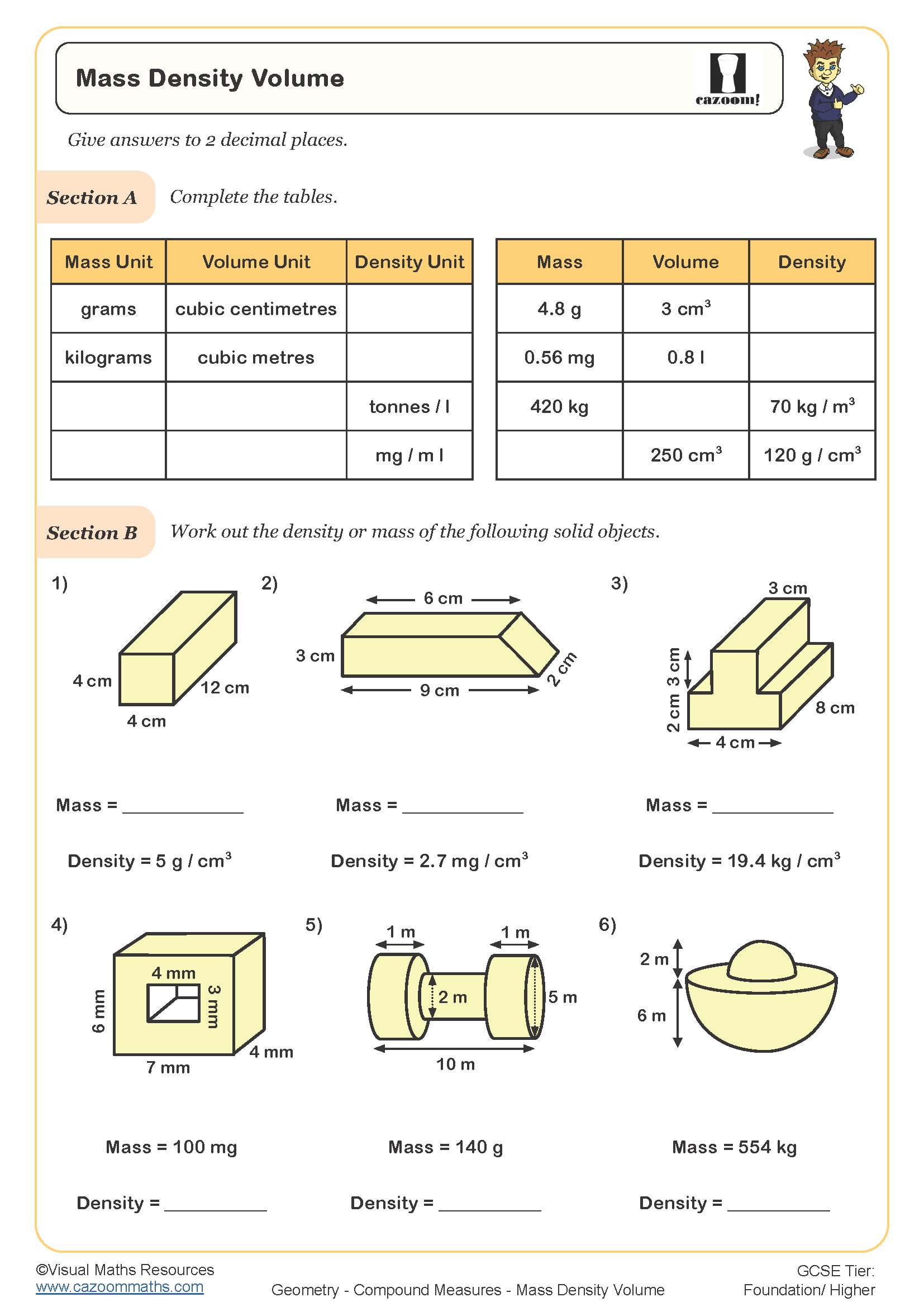
The formula for calculating density is straightforward:
Density = Mass/Volume
In this equation, mass is measured in kilograms or grams, while volume is measured in cubic meters or cubic centimeters. This formula allows us to determine how tightly packed the particles within a substance are, which is critical for understanding its behavior under different conditions.
Why is Density Important?
Density plays an essential role in various scientific and engineering applications. Here are some reasons why understanding density is important:
- Buoyancy: An object’s density determines whether it will float or sink in a fluid. Objects with a density lower than the fluid will float, while denser objects will sink.
- Material Selection: Engineers consider density when selecting materials for construction, as it affects strength, weight, and stability.
- Identification: Density can help identify substances, as each material has a characteristic density.
- Population Studies: In geography, density is used to describe the number of people living in a given area, known as population density.
Density in Everyday Life
Density is a concept we encounter in everyday life, often without realizing it. For instance, when you add ice cubes to a glass of water, they float because the density of ice is less than that of liquid water. Similarly, when oil is poured into water, it floats on top because it is less dense.
Applications of Density
Density is a versatile concept that finds application across various fields:
In Physics and Chemistry
In physics and chemistry, density is used to predict how substances will interact. For example, in chemical reactions, knowing the density of reactants and products can help in calculating yields and understanding reaction dynamics.
In Engineering
Engineers use density to design structures and machinery. For instance, the density of materials affects the load-bearing capacity of buildings and the efficiency of engines. Understanding the density of different materials helps engineers make informed decisions about which materials to use in specific applications.
In Environmental Science
Density is crucial in environmental science for understanding phenomena such as ocean currents and atmospheric pressure. The density of seawater, influenced by temperature and salinity, affects ocean circulation patterns, which in turn influence climate and weather systems.

In Geology
Geologists use density to study the composition of Earth’s layers. By measuring the density of rocks and minerals, scientists can infer the processes that formed them and the conditions under which they were created.
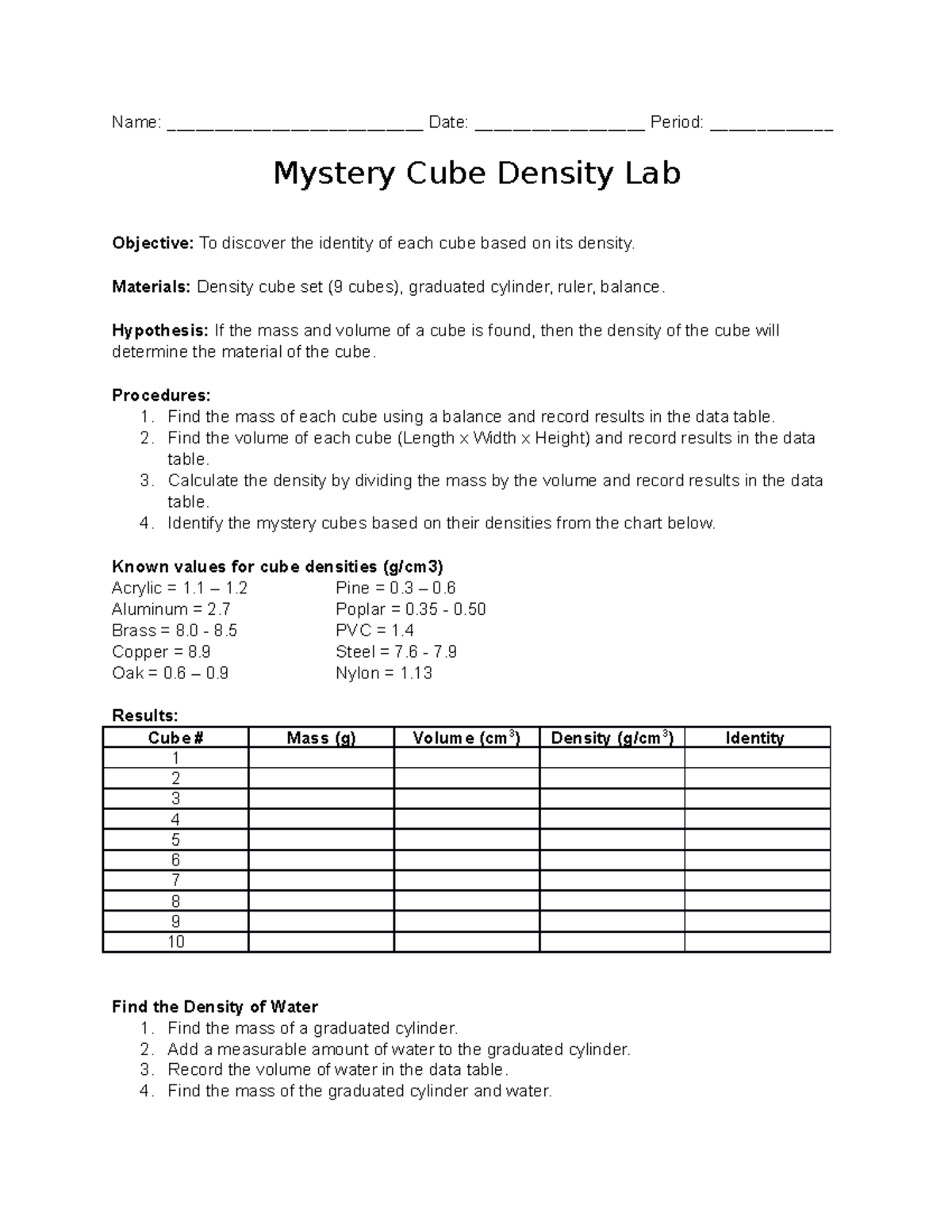
Calculating Density: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating density involves a few simple steps:
- Measure the Mass: Use a scale to measure the mass of the object or substance in kilograms or grams.
- Determine the Volume: Measure the volume of the object. For regular shapes, use mathematical formulas, and for irregular shapes, use water displacement methods.
- Apply the Formula: Divide the mass by the volume to find the density.
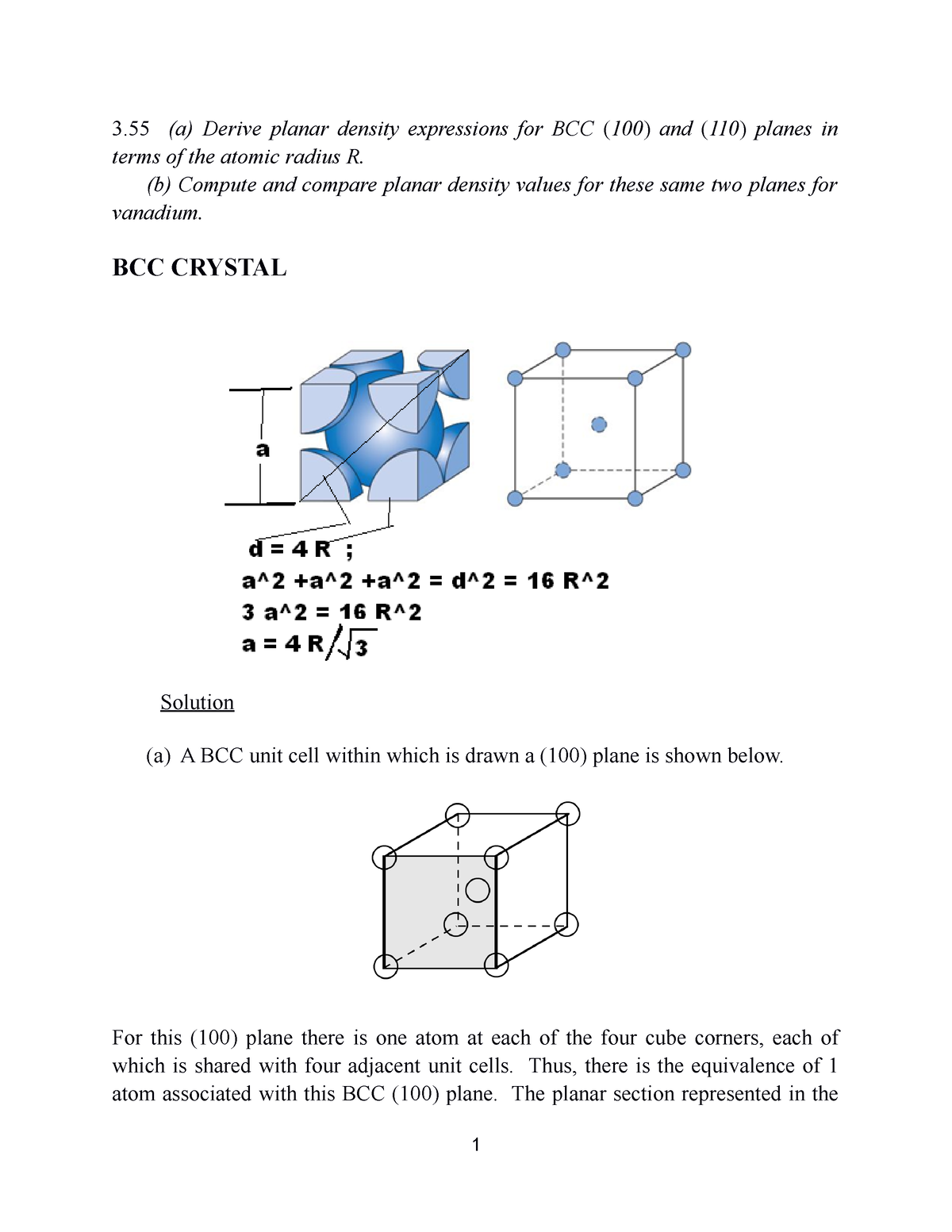
Factors Affecting Density
Several factors can influence the density of a substance:
- Temperature: Generally, as temperature increases, density decreases because the substance expands, increasing its volume.
- Pressure: Increasing pressure can increase density by compressing the substance into a smaller volume.
- Composition: The type and arrangement of atoms or molecules in a substance affect its density.
Understanding what density is and how it applies to different fields is crucial for both scientific exploration and practical applications. From floating icebergs to the design of skyscrapers, density is a key factor that influences the world around us. By mastering the concept of density, we gain insights into the fundamental properties of materials and the forces that shape our environment.